BOSULIF is a prescription medicine used to treat:
- children 1 year of age and older who have a certain type of leukemia called chronic phase (CP) Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (Ph+ CML) who are newly diagnosed or who no longer benefit from or did not tolerate other treatment.
It is not known if BOSULIF is safe and effective in children less than 1 year of age with CP Ph+ CML who are newly diagnosed or who no longer benefit from or did not tolerate other treatment or in children with AP Ph+ CML or BP Ph+ CML.

How Pediatric Patients with CML Responded to BOSULIF in a Clinical Trial
STUDY RESULTS FOR BOSULIF
- Results in pediatric patients who were newly diagnosed
- Results in pediatric patients who no longer benefited from or did not tolerate other treatment
BOSULIF was studied in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed CP Ph+ CML. Doctors or healthcare professionals (HCPs) took samples of patients’ blood and bone marrow regularly and looked at the level of major cytogenetic response (MCyR), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), and major molecular response (MMR).


A cytogenetic response measures the decrease in the number of Philadelphia chromosomes in leukemia cells. MCyR is when no more than 35% of the cells in the bone marrow have the Philadelphia chromosome. CCyR is when no cells with the Philadelphia chromosome can be found in the bone marrow.
A molecular response measures the BCR-ABL gene in the blood. MMR is when the amount of BCR-ABL gene in the blood is below ≤ 0.1%.
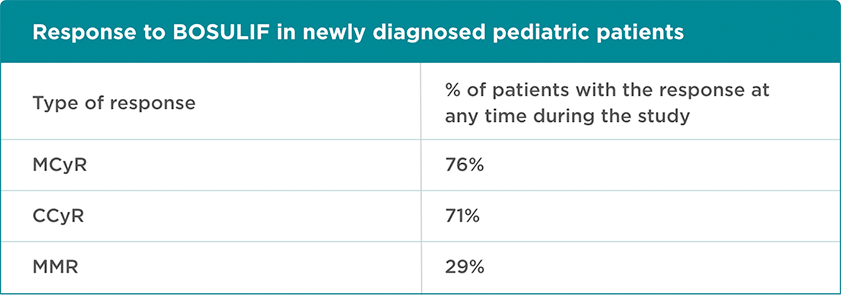
21 newly diagnosed patients were enrolled in the trial. Their median* age was 14 years (range, 5 to 17 years).
*The median is the “middle value” in a list of numbers. It is a kind of measurement. For example, half of the patients in the study were older than the median age, and half were younger.
BOSULIF was studied in pediatric patients with CP Ph+ CML who had been treated with 1 or more prior TKIs. Doctors or healthcare professionals (HCPs) took samples of patients’ blood and bone marrow regularly and looked at the level of major cytogenetic response (MCyR), complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), major molecular response (MMR), and deep molecular response (MR4.5).
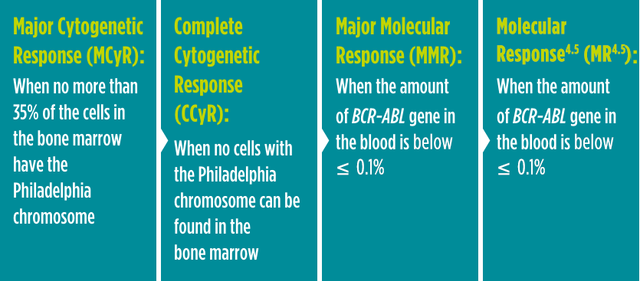
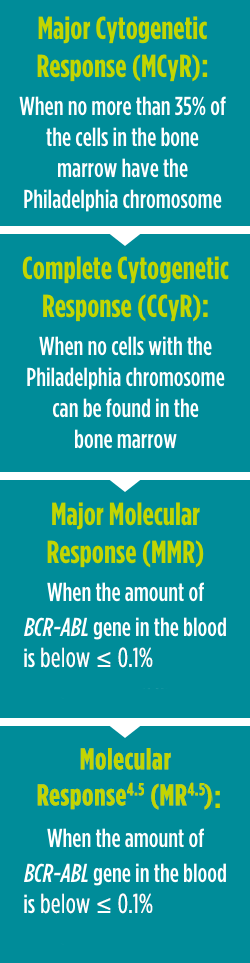
A cytogenetic response measures the decrease in the number of Philadelphia chromosomes in leukemia cells. MCyR is when no more than 35% of the cells in the bone marrow have the Philadelphia chromosome. CCyR is when no cells with the Philadelphia chromosome can be found in the bone marrow.
A molecular response measures the BCR-ABL gene in the blood. MMR is when the amount of BCR-ABL gene in the blood is below ≤ 0.1%.
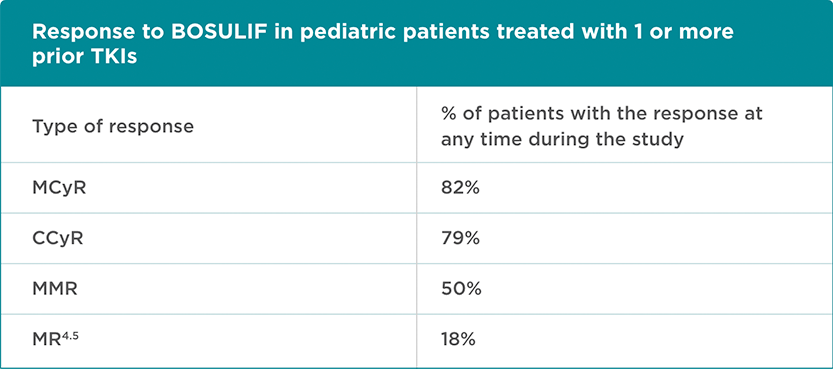
28 patients who had been treated with 1 or more prior TKIs were enrolled in the trial. Their median* age was 11 ½ years (range, 1-17 years).
*The median is the “middle value” in a list of numbers. It is a kind of measurement. For example, half of the patients in the study were older than the median age, and half were younger.




