Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Philadelphia chromosome–positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML)?
CML is typically caused by an abnormal chromosome called the Philadelphia chromosome. If your CML is caused by this chromosome, it may also be referred to as Ph+ CML. This abnormal chromosome produces an abnormal protein called BCR-ABL. BCR-ABL causes the bone marrow to grow and divide out of control.
2. How does BOSULIF work?
BOSULIF is a type of drug called a protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). BOSULIF blocks the abnormal BCR-ABL protein made by CML cells that have the Philadelphia chromosome and helps prevent the creation of leukemia cells.
3. How can I track the progress of my treatment?
Frequent monitoring and blood tests are very important, so ask your doctor or healthcare professional (HCP) about getting tests that gauge the status of your disease and how you are responding to treatment.
Monitoring with quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) every 3 months is recommended for all patients after initiating therapy, including those who meet response milestones at 3, 6, and 12 months.
How often you will have these tests will be determined by your doctor or HCP. Talk to your doctor or HCP about any questions or concerns you may have about these tests.
4. What are the potential side effects associated with taking BOSULIF?
BOSULIF may cause a range of side effects. It’s important to be aware of the side effects so you know what may occur.
BOSULIF may cause serious side effects, including:
- Stomach problems. BOSULIF may cause stomach (abdomen) pain, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, or blood in your stools. Get medical help right away for any stomach problems
- Low blood cell counts. BOSULIF may cause low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia), low red blood cell counts (anemia), and low white blood cell counts (neutropenia). Your doctor should do blood tests to check your blood cell counts regularly during your treatment with BOSULIF. Call your doctor right away if you have unexpected bleeding or bruising, blood in your urine or stools, fever, or any signs of an infection
- Liver problems. Your doctor should do blood tests to check your liver function regularly during your treatment with BOSULIF. Call your doctor right away if your skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow (jaundice), or you have dark “tea color” urine
- Heart problems. BOSULIF may cause heart problems, including heart failure and decreased blood flow to the heart, which can lead to heart attack. Get medical help right away if you get shortness of breath, weight gain, chest pain, or swelling in your hands, ankles, or feet
- Your body may hold too much fluid (fluid retention). Fluid may build up in the lining of your lungs, the sac around your heart, or your stomach cavity. Get medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms during your treatment with BOSULIF:
- shortness of breath and cough
- chest pain
- swelling in your hands, ankles, or feet
- swelling all over your body
- weight gain
- Kidney problems. Your doctor should do tests to check your kidney function when you start treatment with BOSULIF and during your treatment. Call your doctor right away if you get any of the following symptoms during your treatment with BOSULIF:
- you urinate more or less often than normal
- you make a much larger or smaller amount of urine than normal
The most common side effects of BOSULIF in adults and children with CML include diarrhea, stomach (abdominal) pain, vomiting, nausea, rash, tiredness, liver problems, headache, fever, decreased appetite, respiratory tract infections (infections in nose, throat, or lungs), constipation, and changes in certain blood tests. Your doctor may do blood tests during treatment with BOSULIF to check for changes.
Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you get respiratory tract infections, loss of appetite, headache, dizziness, back pain, joint pain, rash, or itching while taking BOSULIF. These may be symptoms of a severe allergic reaction.
Your doctor may change your dose, temporarily stop, or permanently stop treatment with BOSULIF if you have certain side effects.
BOSULIF may cause fertility problems in both female and male patients. This may affect your ability to have a child. Talk to your doctor if this is a concern for you.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of BOSULIF. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
5. How should I take BOSULIF?
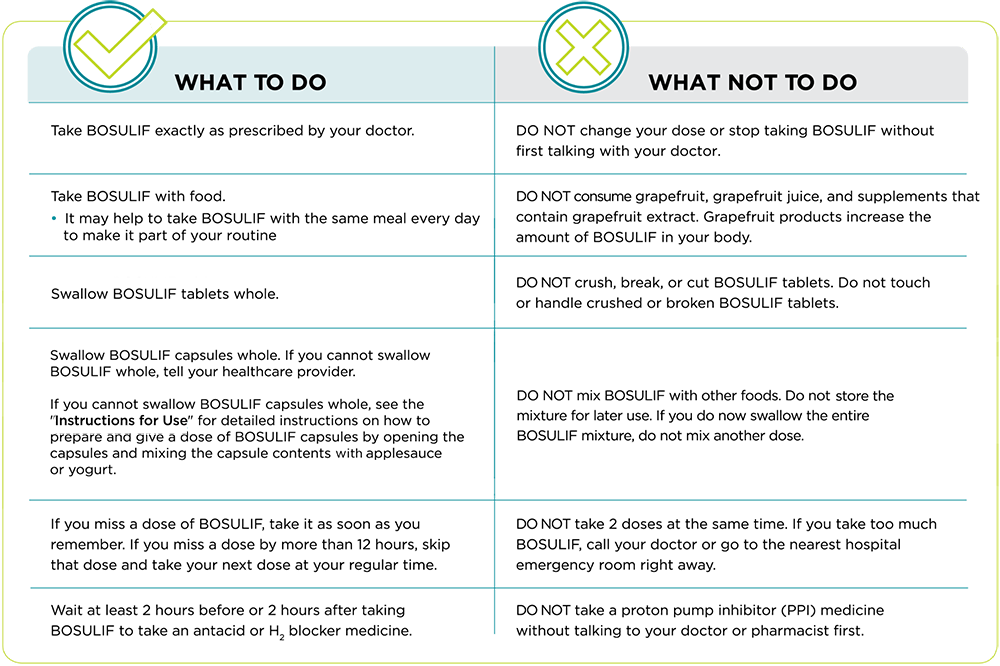
It is important to take BOSULIF exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow the instructions below and talk with your doctor or HCP for more information.
BOSULIF is taken by mouth once a day
BOSULIF should be taken with food
Swallow BOSULIF tablets whole
Swallow BOSULIF capsules whole
Make Sure to Take BOSULIF as Prescribed
When you take BOSULIF...

Terms to Knowa
Accelerated phaseb: The stage of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) when 10% to 19% of cancer cells in blood and bone marrow are blast cells.
BCR-ABL: An abnormal protein that causes the bone marrow to produce leukemia cells.
Blast phaseb: The stage of CML when 20% or more of the cells in the blood or bone marrow are blast cells.
Bone marrow: The soft, sponge-like tissue in the center of most bones. It makes white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
Chromosome: Part of a cell that holds genetic information.
Chronic phaseb: The phase of CML that most patients are diagnosed in. In this phase, less than 10% of the cells in the blood or bone marrow are blast cells.
Complete hematologic response: A return of blood cells to normal levels.
Complete cytogenetic response (CCyR): When there are no cells with the Philadelphia chromosome (Ph+) in your bone marrow.
H2 blockers: Medicines that reduce the amount of stomach acid in the lining of your stomach.
Intolerance: When a patient can no longer take his or her current medicine due to side effects.
Molecular response: A decrease in the percentage of blood cells containing BCR-ABL.
Newly diagnosed: When a patient is being treated for his or her cancer for the first time.
Philadelphia chromosome: An abnormality in your chromosome that results in the production of BCR-ABL protein. This protein causes leukemia cells to grow uncontrollably.
Proton pump inhibitor: A substance used to treat certain disorders of the stomach and intestines, such as heartburn and ulcers.
Resistance: When your disease fails to respond or stops responding to a given therapy.
Severe diarrhea: Severe diarrhea is an increase of greater than or equal to 7 stools/day over baseline
or pretreatment.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): In CML, a TKI is used to block the activity of BCR-ABL protein (a tyrosine kinase); this slows leukemia cell growth.
aUnless otherwise noted, the definitions above are from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) or adapted from the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (LLS) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
bThe phase definitions above are from the World Health Organization (WHO). Some doctors may use different definitions. Talk to your doctor about any questions or concerns you may have about the different phases.
Reminders to Make the Most of Your Treatment
Make sure to tell your doctor or HCP of any changes in:
Your medicines or any new medicines you start taking.
Side effects, including ones that bother you or do not go away.
How you are feeling, even if you think it is not related to your CML.
Your lifestyle, including any new health issues that may arise.
Start a routine
Take your medicine at the same time every day. Consider taking BOSULIF® (bosutinib) in the morning with breakfast or in the evening with dinner.
Use alarms and calendars as reminders to take medicine.
Use a pill container to organize your medicines at home and when you travel.
Your doctor or HCP can help you with side effects
When you start treatment, consider asking your doctor how to prepare for possible episodes of diarrhea, the most common side effect of BOSULIF.
Dose adjustments from your doctor, lifestyle management, and monitoring over time may help you manage side effects.




